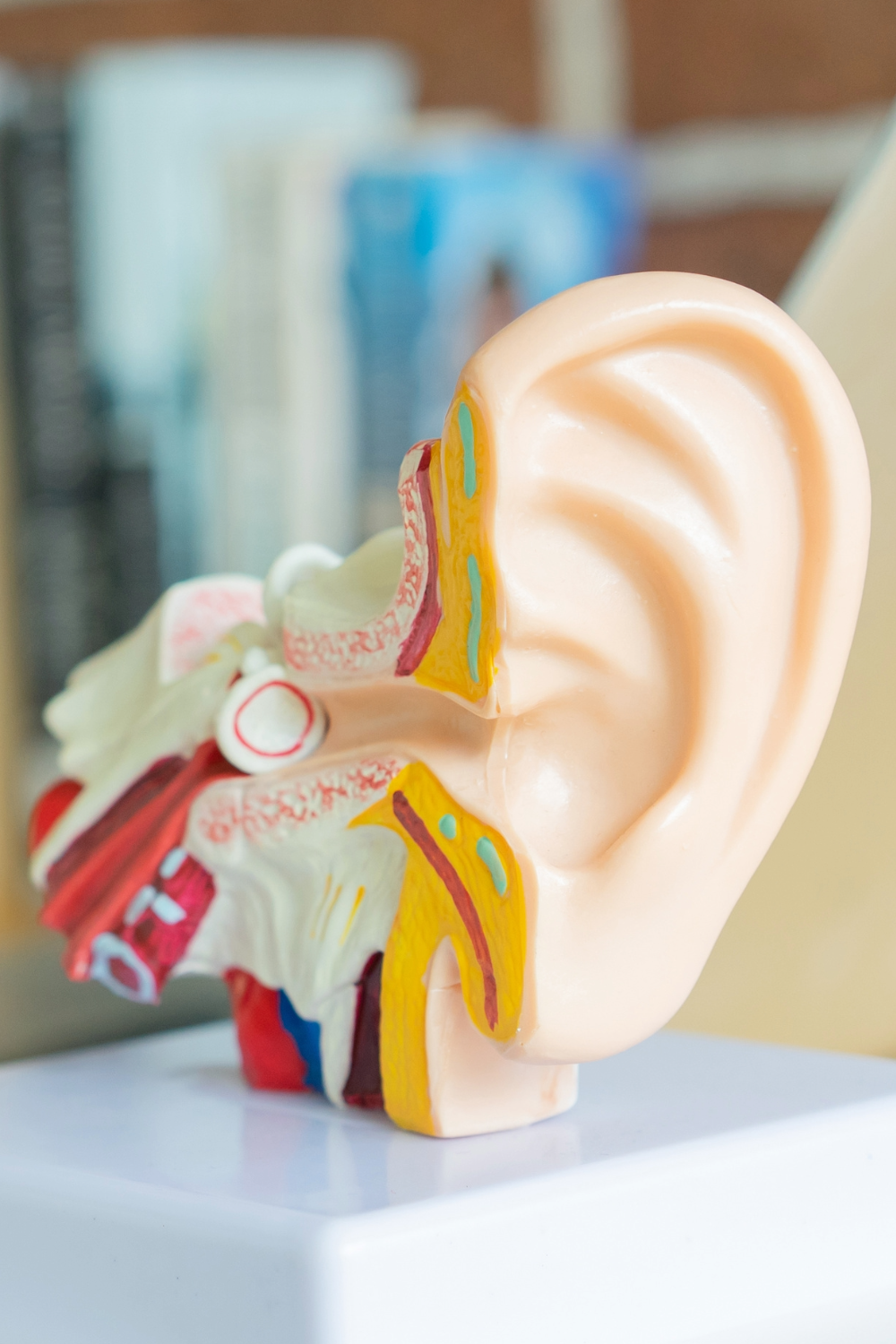
Hearing Assessments
At Auditory Health Care, we believe that everyone, from infants to seniors, deserves a clear connection to the world around them. Our comprehensive hearing assessments cater to ages 6 months to 109 years, ensuring each individual receives the attention they need. We proudly participate in the Infant Screening Program, and offer personalized hearing rehabilitation services to enhance your auditory experience.
UNDERSTANDING HEARING IMPAIRMENTS
Early Detection is Key
Did you know that approximately 10% of the population - 20% of those over 65 and 40% of those over 75 - have a significant hearing problem? Hearing loss is the third most prevalent chronic disability among older adults, as both the incidence and prevalence of hearing loss increases with age. Hearing impairment can begin as early as the third or fourth decade of life, developing gradually and often going unnoticed. Hearing loss can also present at birth or in early childhood, leading to potential delays in speech and language development if not addressed.
Early detection is crucial! Early identification of hearing loss leads to better success with amplification. Don’t wait to improve your or a loved one's hearing experience - schedule your assessment today and take the first step towards better auditory health!
WHAT IS YOUR HEARING HANDICAP?
Questions to Help Evaluate
We believe that understanding your hearing health is the first step towards better communication and quality of life. Complete this simple 25-question quiz from the comfort of your home to help you identify potential hearing challenges, paving the way for a personalized assessment.
01.
Does a hearing problem cause you to use the phone less often than you would like?
02.
Does a hearing problem cause you to feel embarrassed when meeting new people?
03.
Does a hearing problem cause you to avoid groups of people?
04.
Does a hearing problem make you irritable?
05.
Does a hearing problem cause you to feel frustrated when talking to members of your family?
06.
Does a hearing problem cause you difficulty when attending a party?
Three Types of Hearing Impairments
01
Conductive Hearing Loss
- Conductive Hearing Loss occurs in the outer & middle ear.
- Common causes include ear infections, excessive ear wax or fluid build up, damage to the ear drum (perforation) or issues with middle ear ossicles (tiny ear bones).
- Symptoms of this type of impairment can include muffled hearing or difficulty hearing faint sounds, ears feeling "full" or blocked, and ability to hear better in noisy environments over quiet ones.
- It is generally temporary and usually treatable through removal of any blockages, medication for infections, surgery for structural problems and in some cases, the use of hearing aids.
02
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss occurs in the inner ear (cochlea) or auditory nerve; the majority of people with hearing impairments have this type of loss.
- Common causes include the natural aging process, excessive noise exposure (loud sounds damaging hair cells), viral or bacterial infections, genetic conditions, head trauma, auditory nerve tumours and medications harmful to hearing (ototoxic drugs).
- Symptoms of this type of impairment can include difficulty hearing in noisy environments, muffled or distorted sounds, trouble understanding speech or high-pitched sounds and permanent loss of hearing.
- It is usually permanent but can often be assisted with the use of hearing aids or assistive listening devices, and cochlear implants for severe cases.
03
Central/Mixed Hearing Loss
- Central Hearing Loss is a combination of conductive (outer/middle ear) and sensorineural (inner ear or auditory nerve) hearing impairments.
- Common causes include a mix of factors affecting both parts of the ear (such as age-related loss combined with an ear infection or wax build up), trauma affecting different ear structures and chronic ear conditions.
- Symptoms of this type of impairment includes a combination of conductive and sensorineural symptoms, and may also manifest as challenges in language recognition.
- It is usually permanent but can often be assisted with the use of auditory technical devices or cochlear implants.
Conductive Hearing Loss
- Conductive Hearing Loss occurs in the outer & middle ear.
- Common causes include ear infections, excessive ear wax or fluid build up, damage to the ear drum (perforation) or issues with middle ear ossicles (tiny ear bones).
- Symptoms of this type of impairment can include muffled hearing or difficulty hearing faint sounds, ears feeling "full" or blocked, and ability to hear better in noisy environments over quiet ones.
- It is generally temporary and usually treatable through removal of any blockages, medication for infections, surgery for structural problems and in some cases, the use of hearing aids.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss occurs in the inner ear (cochlea) or auditory nerve; the majority of people with hearing impairments have this type of loss.
- Common causes include the natural aging process, excessive noise exposure (loud sounds damaging hair cells), viral or bacterial infections, genetic conditions, head trauma, auditory nerve tumours and medications harmful to hearing (ototoxic drugs).
- Symptoms of this type of impairment can include difficulty hearing in noisy environments, muffled or distorted sounds, trouble understanding speech or high-pitched sounds and permanent loss of hearing.
- It is usually permanent but can often be assisted with the use of hearing aids or assistive listening devices, and cochlear implants for severe cases.
Central/Mixed Hearing Loss
- Central Hearing Loss is a combination of conductive (outer/middle ear) and sensorineural (inner ear or auditory nerve) hearing impairments.
- Common causes include a mix of factors affecting both parts of the ear (such as age-related loss combined with an ear infection or wax build up), trauma affecting different ear structures and chronic ear conditions.
- Symptoms of this type of impairment includes a combination of conductive and sensorineural symptoms, and may also manifest as challenges in language recognition.
- It is usually permanent but can often be assisted with the use of auditory technical devices or cochlear implants.
Effective Tinnitus Management
Tinnitus is the perception of ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the ears that aren’t caused by external noise. It can range from a minor irritation to a major disruption in daily life. Symptoms include hearing persistent or intermittent sounds, which may be loud or soft, and often occur in quiet settings. While there’s no cure for tinnitus, it can be managed through sound therapy, hearing aids, or counseling. If you're experiencing these symptoms, book an assessment today to find the right treatment plan and improve your quality of life.
COMPREHENSIVE HEARING EVALUATION
The Hearing Test Process
Understand the different evaluations we conduct to provide a comprehensive evaluation of ear and hearing health, contributing to accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans for your needs.
Otoscopy (Physical Exam)
Otoscopy is a physical examination of the ears - a visual inspection of the outer ear, ear canal and eardrum using an otoscope. This exam detects signs of ear infections, blockages, ear drum perforation and structural abnormalities.
Immittance/Tympanometry
Immittance testing evaluates the function of the middle ear and the mobility of the eardrum. It includes tests like tympanometry (eardrum movement in response to pressure changes) and acoustic reflex testing (muscle response to loud soundes). This helps to diagnose issues such as fluid buildup or blockages, eardrum perforations or middle ear dysfunctions.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs)
Distortion Product Otoacoustic (DPO) Emissions is a non-behavioural test that evaluates how well the cochlea (inner ear) functions by measuring sound waves produced by the ear itself in response to tones. This test detects cochlear damage or hair cell dysfunction and is often used for newborn screening or individuals unable to respond to behavioral tests as no active response from the patient is required.
Pure-Tone Audiometry
Pure-Tone Audiometry, or Threshold Sensitivity Testing, is a common test used to determine the quietest sounds a person can hear at various pitches (frequencies) and volumes. Conducted in a soundproof booth, the patient wears headphones and signals when they hear a tone.
For older children and adults, signaling typically involves pressing a button or raising a hand. For younger children who may not be able to follow these instructions, play audiometry techniques are used. These involve engaging activities like placing a block in a bucket or completing a puzzle piece each time a sound is heard, making the process interactive and fun. For infants or very young children who cannot signal, visual reinforcement audiometry (VRA) is often used. In VRA, the child is conditioned to turn their head toward a sound, and a visual reward, such as a light-up toy or animated character, reinforces the behavior. These tailored approaches ensure accurate testing for all ages and help identify the type and degree of hearing loss (conductive, sensorineural, or mixed), enabling effective treatment planning.
Speech/Noise Testing
Speech/Noise Testing measures how well a person can hear and understand speech at different volumes and in noisy environments. The test involves listening to sentences or words with and without background noise and repeating them. This helps assess the real-world impact of hearing loss, particularly in noisy settings, and aids in treatment planning.
Hearing 101:
What You Should Know
Get the facts to help you make an informed decision about your hearing health.
Untreated Hearing Loss
ButtonFrequently Asked Questions
-
Can I book a hearing test or do I need a referral?
You can schedule a hearing assessment directly with our clinic. No physician referral is required.
-
How long is the appointment?
We are a patient centered, full-service clinic, so some appointments require more time than others.
A baseline hearing assessment typically takes around 45 minutes, while comprehensive hearing aid evaluations take about 1.5 hours. For quicker services like ear wax removal, appointments usually last around 15 minutes.
Our goal is to ensure each appointment is thorough and tailored to your hearing care needs.
-
What are your hours?
We are open Monday, Tuesday and Thursday from 9:00 am to 5:00 pm. On Wednesday and Friday, we are open from 9:00 am to 3:00 pm. We close daily for lunch from 12:30 to 1:30pm.
-
Is your clinic wheelchair accessible?
We are partially wheelchair accessible. There is an outdoor ramp allowing wheelchair access into our building. Once inside the building, we have a portable ramp when required to allow access into the waiting room. However, there is no wheelchair accessible washroom.
-
Is there a fee for the hearing test?
There is a fee of $80 for a hearing assessment, as they are not covered by OHIP.
Contact your insurance provider to see if you have coverage for audiologist assessments.
-
Why can I get a free hearing test at other clinics?
Auditory Health Care is a privately owned & locally operated clinic. A lot of the other clinics are owned by manufacturers or are part of a chain - usually their clinicians are Hearing Aid Dispensers and not Audiologists. A free hearing test is given to entice you to go to these clinics with the hope you will purchase hearing aids from them.
We are a patient centered care clinic dedicated to provide personalized services for your unique listening needs, and therefore we charge a nominal fee for assessments.
-
Are there programs to help cover the cost of hearing devices?
If you do not have private insurance benefits coverage for hearing devices, there are several associations that may help:
Ontario Assistive Devices Program: www.ontario.ca/page/hearing-devices
VOICE for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Children: www.voicefordeafkids.com
WSIB (Workplace Safety & Insurance):
*for noise induced hearing loss
Veterans Affairs Department:
Social Services:
ACSD, ODSP and Ontario Works
-
What hearing aids or brands do you sell?
We have a relationship with all hearing aid manufacturers. As a privately owned clinic, we are not specifically tied to any one manufacturer and therefore can prescribe and dispense what is deemed most appropriate.
When our Audiologist, Mandy, prescribes a hearing aid she bases this decision on several factors:
- First, of course, is your hearing loss. Not all hearing aid styles and technologies are appropriate for all hearing losses.
- Second is your listening environment - someone who is still active and in a variety of difficult listening situations may have different listening needs than someone who is mostly using the hearing aids to watch tv, or for one-on-one conversations.
- Third is your manual dexterity - the smaller the hearing aids, the more difficult they are to manipulate; having to change batteries more often due to smaller battery size, etc.
- Fourth is your budget - there are many levels of technology at different price points. It is important that you feel comfortable with the amount of money you are having to spend.
Once Mandy has obtained all this information, she can then make an informed hearing aid prescription.
-
Can I walk in without making an appointment in advance?
Hearing device clean & check services are available as a walk-in service. All other services are available by appointment only.
-
When can I get an appointment to see the Audiologist?
This depends on the type of appointment required. An appointment for cerumen (earwax) removal, a hearing aid follow-up, a check of middle ear status, or an office consult are relatively short appointments and therefore, can be made with less notice. A full assessment is a longer appointment, and therefore we generally schedule these 3-5 months in advance.
-
Why are you scheduling so far in advance?
As a comprehensive assessment requires additional procedures and a personal needs consultation, we generally schedule a few months in advance. However, please feel free contact the office to discuss the specific nature of your needs, as some types of appointments can be fast-tracked for medical reasons (such as sudden hearing loss).
-
What is the process of getting hearing aids?
The first step is to schedule the hearing evaluation. The initial appointment is approximately an hour and a half in length. During that appointment you will have a complete hearing assessment, discussion of results, and treatment recommendations.
Depending on the results, our Audiologist, Mandy, may do a recommendation to your family doctor to begin the referral process to an otolaryngologist. Symptoms that may require referral to an ear, nose and throat specialist include:
- Persistent sore throat
- Runny nose that doesn’t go away
- Chronic cough
- Chronic sinus pressure or nasal congestion
- Dizziness
- Vertigo
- Severe allergies
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Hearing loss
- Hoarseness or wheezing that doesn’t go away
- Frequent ear infections
- Chronic tonsillitis
- A lump on your face or neck
- Severe snoring
- Sleep apnea
If hearing aids are recommended, our program of care involves multiple appointments during the 90-day trial period. Following the trial period a 3-month check up, followed by an annual checkup is scheduled. An updated hearing test is recommended every 1-2 years or event driven as needed.
If there are any concerns at any other time, we recommend you contact our office for assistance. We are always happy to help!
-
What is the difference between an Audiologist and a Hearing Aid Dispenser?
Both audiologists and hearing instrument practitioners conduct hearing tests for the purposes of dispensing hearing aids and other assistive listening devices. Despite sharing this similarity, the hearing instrument practitioner’s scope of practice is narrower than the audiologist’s.
Hearing instrument practitioners test peripheral hearing for the purpose of selecting, fitting and dispensing hearing aids and other assistive listening devices. Hearing instrument practitioners are typically not permitted to provide services to children (age-range defined differently in various provinces & territories) as their scope is generally limited to adults and is reflected as such in regulation, where it exists.
Audiologists are uniquely qualified to assess, identify, diagnose (restricted in some provinces) and manage individuals with peripheral or central hearing loss, hyperacusis, tinnitus and balance disorders; and to select, prescribe, fit and dispense hearing aids and other assistive listening devices. Audiologists also receive extensive training in counseling and (re)habilitation, which extends their practice beyond the selection and fitting of amplification. Audiologists are trained to perform these services for all ages – from newborns to adults.
Don't Let Hearing Loss Go Undetected
If you’re noticing changes in your hearing or that of a loved one, it's time for a thorough hearing assessment. Our expert team is here to evaluate your needs and provide personalized solutions to help you or your loved one hear clearly and comfortably.
Book an Appointment
Contact Us
Thank you for contacting us!
A member of our team will get back to you as soon as possible with availability to book an appointment.
If you do not receive a reply within 2 business days, please give our clinic a call.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later.
The Hearing Clinic
Clinic Hours
- Mon, Tue, Thu
- -
- Wed, Fri
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed
*Closed Daily from 12:30pm-1:30pm